Injection Molding
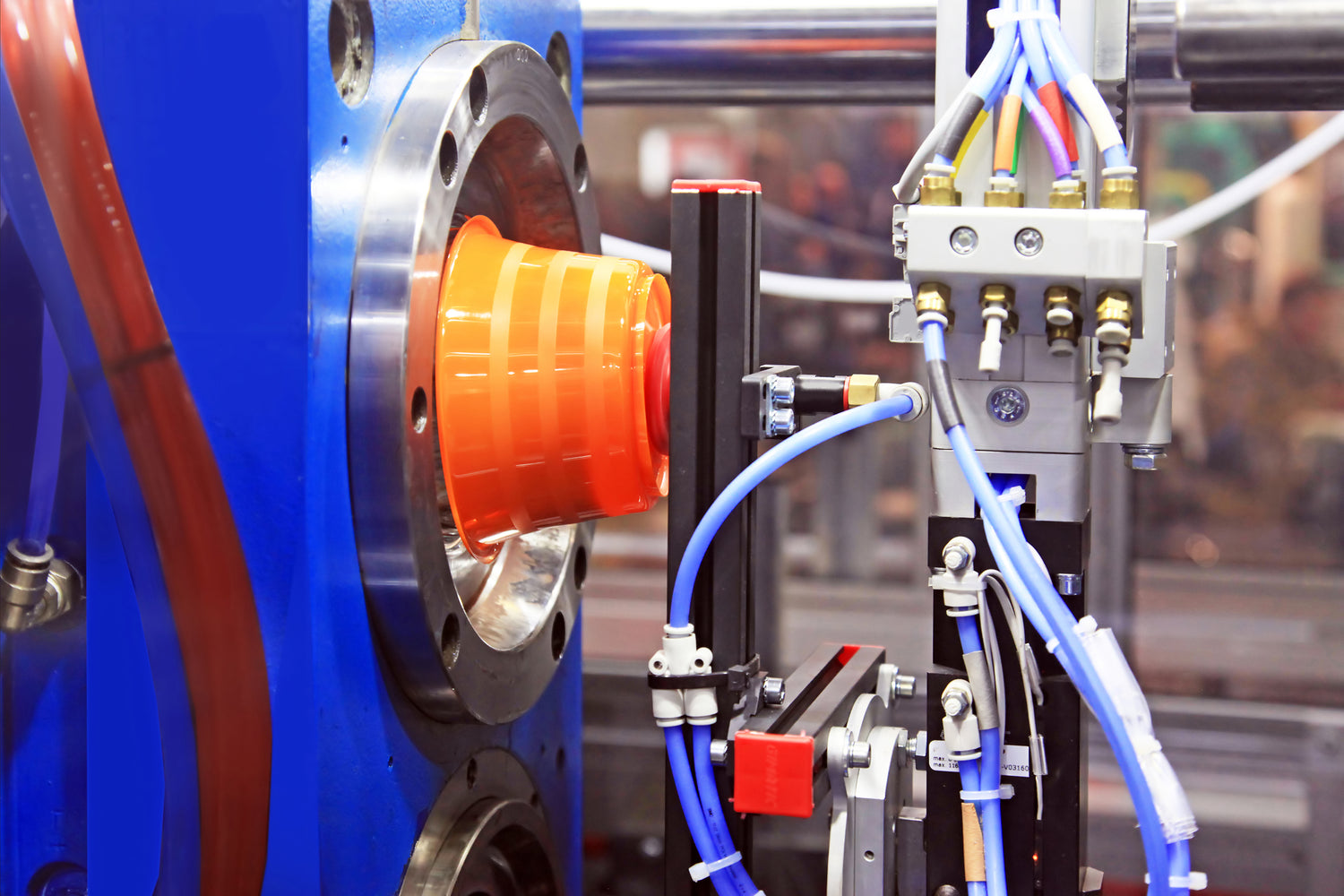
Injection molding is a manufacturing process in which thermoplastic or thermoset material is heated to a molten state and injected under high pressure into a precision-machined mold cavity. Once the material cools and solidifies, the mold opens and the finished part is ejected.
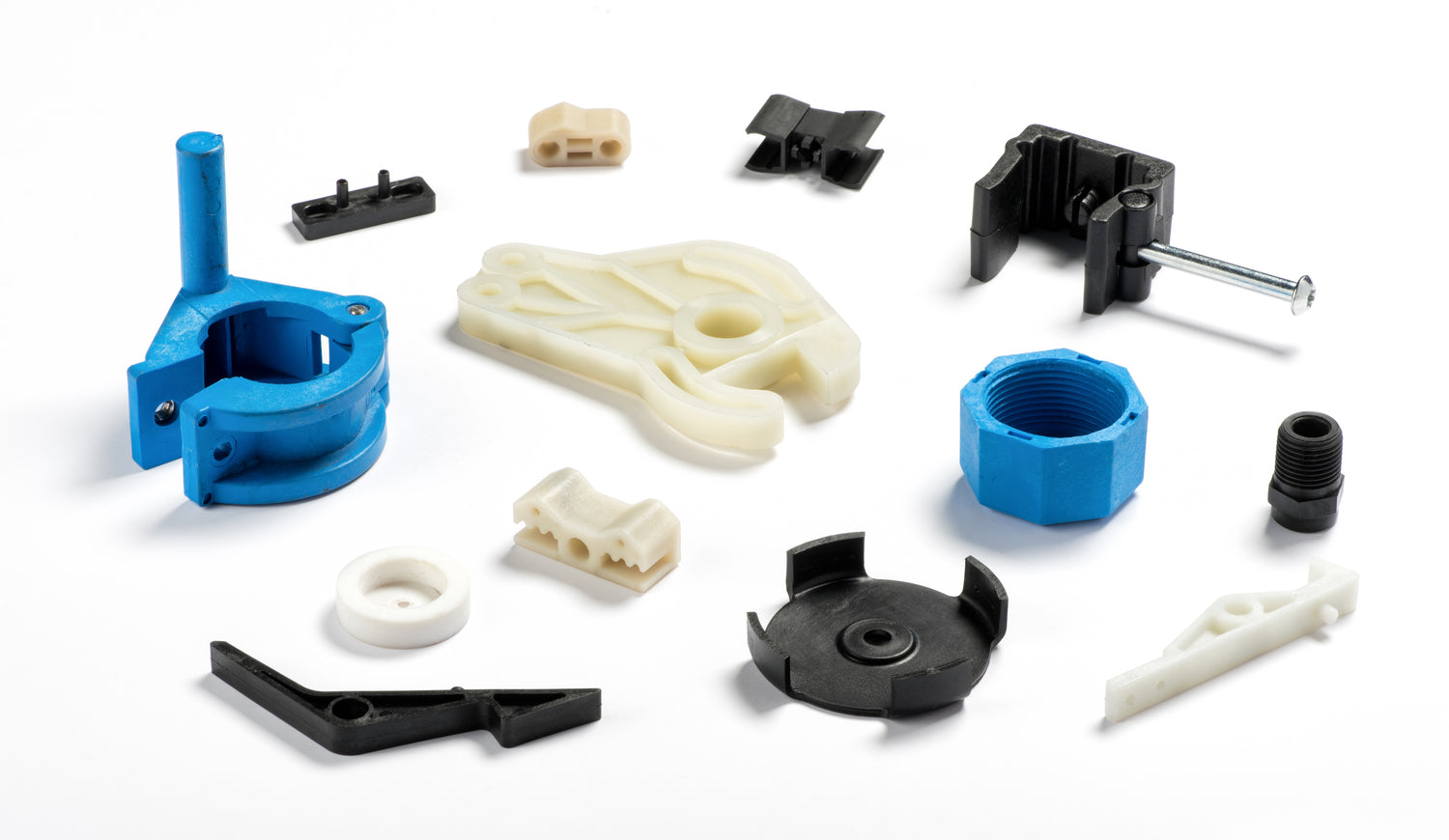

Quick-Turn Injection Molding
Quick turn injection molding is a streamlined version of the traditional injection molding process designed to produce parts faster—often in days instead of weeks.
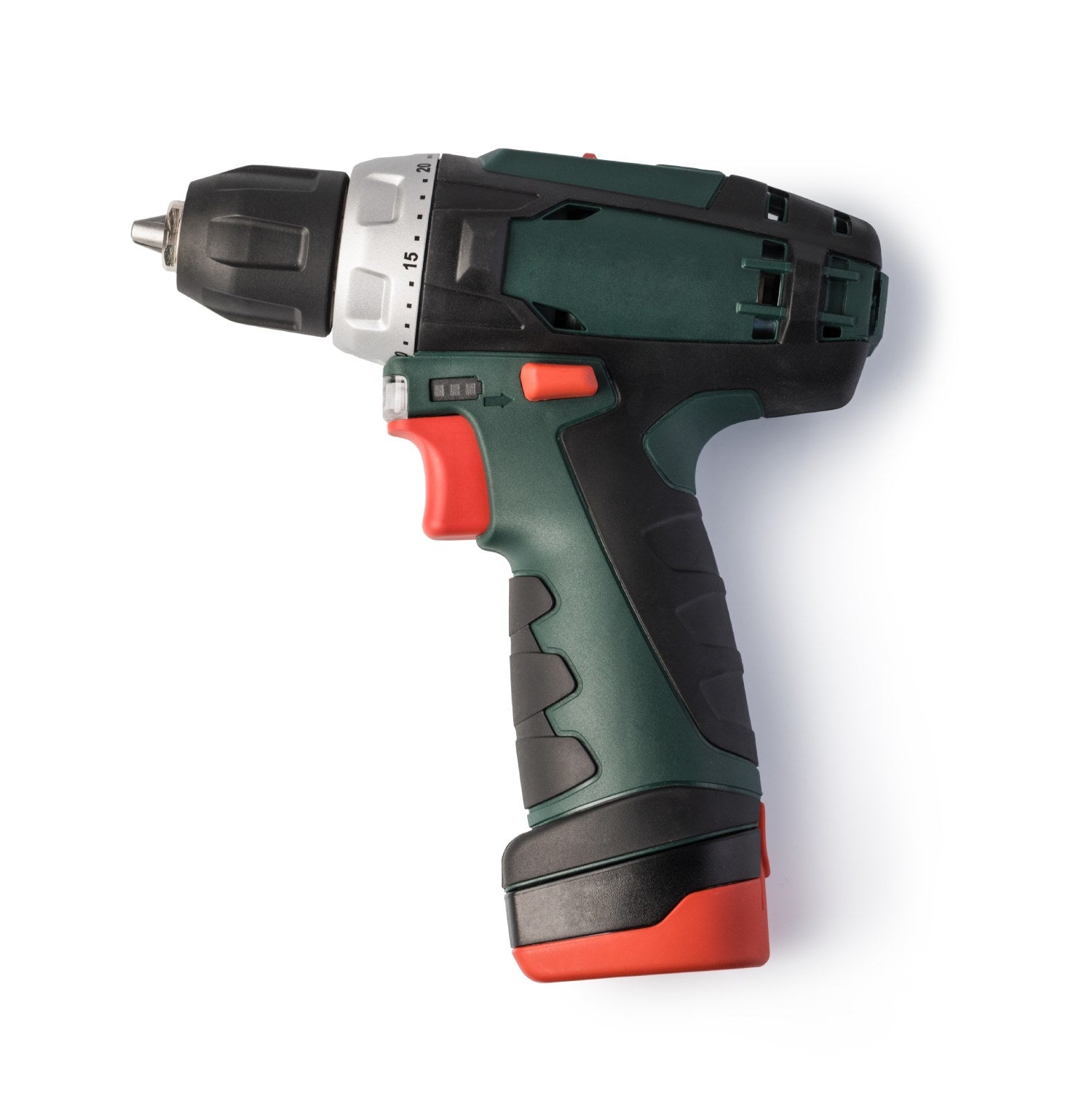

Overmolding
Overmolding is a process where one material, usually a soft plastic or rubber, is molded over another to create a single part with improved grip, comfort, or function—like a rubber handle on a tool.

Insert Molding
Insert molding involves placing a pre-made component, such as a metal insert, into a mold and then injecting plastic around it to permanently bond the materials, often for added strength or embedded features like threads.
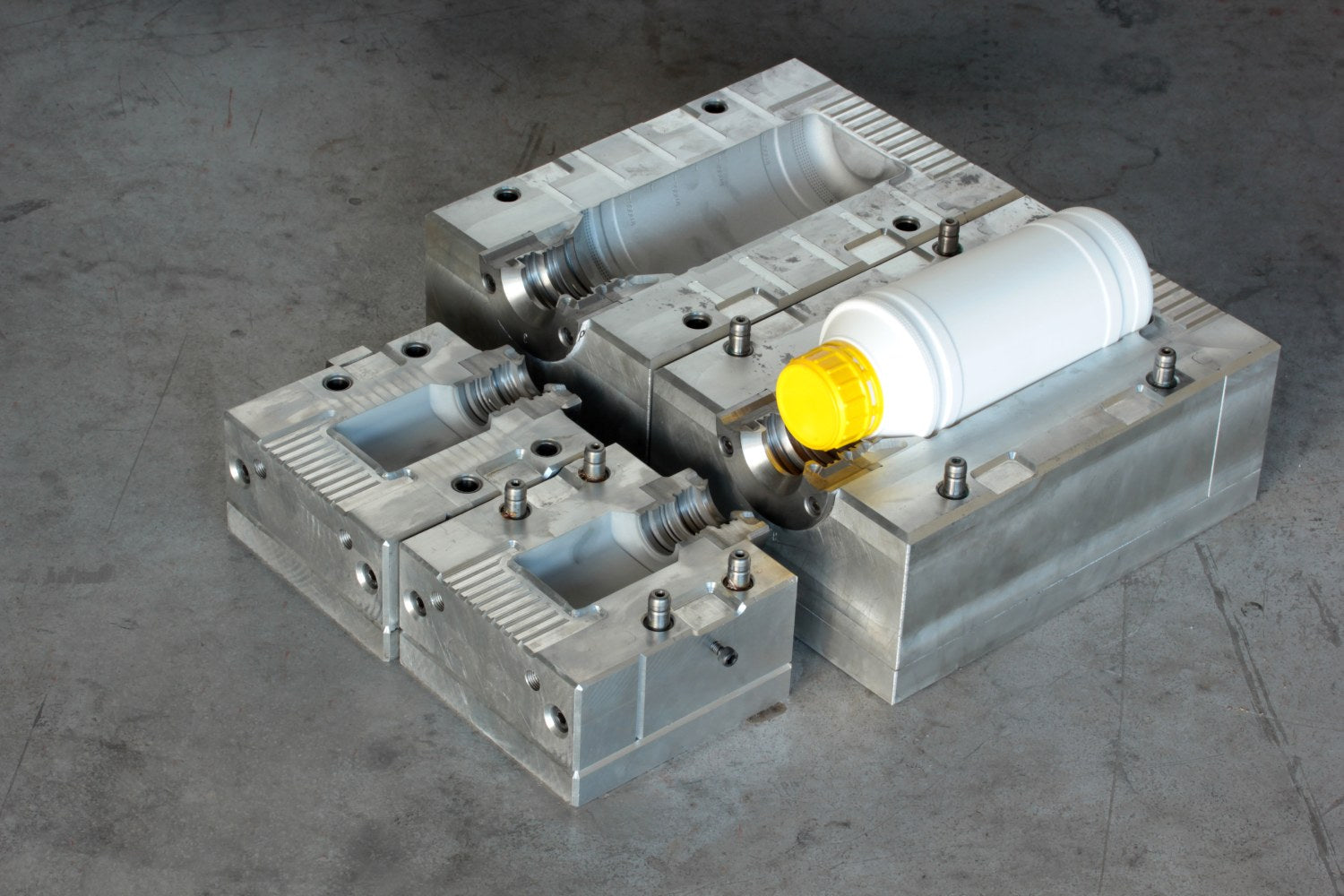
Bridge Molding
Bridge molding is a short-run injection molding process used to "bridge the gap" between prototyping and full-scale production. It allows companies to produce a limited quantity of parts—often hundreds to thousands—using lower-cost, faster-to-make tooling (like aluminum molds) while waiting for final production tools to be completed.

Prototype molding
Prototype molding is the process of creating a temporary, low-cost injection mold to quickly produce sample parts for testing and design validation before full production begins. It’s often used to evaluate fit, function, and manufacturability using production-like materials, without the time and cost of a full production tool.

Production molding
Production molding is the use of high-durability, precision-engineered molds—typically made from hardened steel—to manufacture large volumes of final, end-use parts with consistent quality and tight tolerances.
It’s designed for long-term, high-volume manufacturing where cost per part is low, and the tooling is built to withstand thousands of cycles.
Compression Molding
Compression molding is a manufacturing process where a pre-measured amount of material—usually a thermoset plastic or rubber—is placed into a heated mold cavity, then compressed under high pressure until it takes the shape of the mold and cures.

Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion is a manufacturing process where melted plastic is forced through a shaped die to create continuous lengths of a fixed cross-sectional profile—like tubing, piping, or window frames. As the material exits the die, it cools and hardens into its final shape.
Urethane and Silicone Casting
Urethane and silicone casting are low-volume molding processes that use flexible silicone molds to produce high-quality parts from liquid materials. Urethane casting creates rigid or semi-rigid plastic-like parts, while silicone casting produces soft, rubber-like components.

Micro Molding
Micro molding is a specialized type of injection molding used to produce extremely small, high-precision plastic parts—often just fractions of a gram in weight and measured in microns. It’s commonly used in medical devices, electronics, and other applications where tiny, intricate components are required.





